SHARIAH GOVERNANCE POLICY DOCUMENT (2019)
One of the most anticipated documents by the industry is the renewed Shariah Governance Framework, which was last issued in 2011. Many were waiting with bated breath on what changes were made to the document. I had a quick look at it also and generally, there were a few fine-tuning done to existing regulations.
A quick summary of the points in the Shariah Governance Policy Document (2019) are as follows:
- The responsibilities of the Board of Directors are to approve the policies regarding Shariah governance, oversee the implementation of SAC’s ruling and internal control framework, oversee the performance of senior management and promote a culture of Shariah compliance in the bank.
- The Board of Directors also must interact sufficiently with the Shariah Committee including giving due regards to the Shariah Committee decisions, paying attention to facts and rational and the implication of implementing the decision, with proper conflict resolutions and record of all deliberations on the issues.
- The Board of Directors must also assess the performance of the Shariah Committee formally, at least annually and ensure the remunerations reflect members’ accountabilities.
- The key responsibilities of the Shariah Committee themselves are defined as follows:
- Provide a decision or advice on the application of SAC ruling and BNM standards on Shariah matters
- Provide a decision or advice on matters that requires a reference to be made by the SAC
- Provide a decision or advice on matters that may trigger Shariah Non-Compliant event
- Deliberate and affirm Shariah non-compliant findings
- Endorsing rectification measures for Shariah non-compliance event
- The Shariah Committee shall be accountable for the quality, accuracy and soundness in their decisions and advices.
- The Shariah Committee must establish a robust methodology to guide decision making process including taking into account relevant business and risk practices.
- If Shariah decides to place additional restrictions on the business in applying SAC ruling (meaning : stricter than SAC rulings), the bank must document the deliberation, obtain Board of Directors view on the decision, and immediately notify BNM on the decision.
- The Shariah Committee must exercise objectivity in making a judgement or deriving a decision to avoid impairing professional objectivity. Sufficient time is to be devoted to prepare for and attend Shariah Committee meetings.
- The Shariah Committee must continuously develop reasonable understanding of the business and keep abreast of the latest market and regulatory development, to be led by the Chairman of the Shariah Committee.
- The Chairman of the Shariah Committee must be able to apply relevant procedures for Shariah deliberations, liaise with Board of Directors, ensure sound decisions are made, encourage healthy discussion on issues, and ensure maintenance of records supporting Shariah decisions.
- Shariah Committee meetings must be conducted at least once every 2 months (at least 2 times a year for Islamic Banking Windows operations) and attendance of each member must be 75%. This information to be reported in the bank’s annual report.
- Appointment of the Shariah Committee must fulfil the following:
- the person is a Muslim
- the person is “fit and proper“
- the person is either Shariah qualified person or an expert possessing skills, knowledge and experience (to support the Shariah function)
- Shariah Qualified Person means the person:
- hold a minimum bachelor degree in Shariah which includes studies on Usul Fiqh (principles of Islamic Jurispruedence) or Fiqh Muamalat (Islamic transaction/commercial law)
- possesses solid knowledge in Shariah with reasonable Islamic finance knowledge and experience
- demonstrates strong proficiency and knowledge in written and verbal Arabic.
- A Shariah Committee member shall not serve in the same Bank for more than 9 years, must not accept appointment on more than 1 licensed banks, 1 licensed takaful operator and one prescribed institution. The member must also not be an active politician.
- The Shariah Committee composition must consist of a Shariah qualified Chairman of Shariah Committee and the majority of the Shariah Committee Members are Shariah qualified.
- The Shariah Secretariat must provide the Shariah Committee adequate time to deliberate all Shariah matters.
HOW MUCH POWER DOES THE SHARIAH COMMITTEE REALLY HAVE?
As expected, the Shariah Committee must have full accountability in making decisions via robust deliberation of issues, including considerations of business practices. This idea is consistent with BNM’s expectation that Shariah Committee must reach a certain level of competency in advising the banks. BNM, it seems, is prepared to provide authority for Shariah Committee to decide on the business direction, in line with the overarching SAC decisions. This indicates that the Shariah Committee is meant to be influential in the Islamic Banking industry.
However, BNM also allows the challenge on Shariah Committee decisions if the bank deems the decisions have not taken into considerations the practical and business sense, especially for decisions stricter than the SAC. In such circumstances, the Board of Directors provide a view on the decision, and must be escalated to BNM. To ensure that this scenario does not happen as often, both Shariah Committee and the business must align the understanding on the business direction and mitigate the discrepancies in understanding. The role of the Chairman of the Shariah Committee is important to manage the interactions between the Board of Directors and his Shariah Committee members.
The above underlines the seriousness of the Shariah Committee function. With great powers comes great responsibilities. To hold such authority, the Shariah Committee must reflect quality, accuracy and soundness in all their decision-making.
WILL A SHARIAH COMMITTEE FUNCTION REMAIN A PART-TIME JOB?

Personally, I understand there are challenges for Shariah Committees to devote a sizeable amount of time to provide banks with high quality, fully deliberated decisions that is valuable to all stakeholders. There are still a number of Shariah Committees only choosing to stay in their areas of expertise while concentrating on their day jobs. We hardly see a scholar having a full-fledge research house coming into the market with resources that can support the business requirements of an Islamic Financial Institution (IFI).
Nothing is mentioned on the expected level of research to be done by a Shariah scholar. That level is still left to interpretation although with the requirement to be “conversant in Arabic” implies Shariah scholar should be referring their research and decisions more consistent with global standards, where text, references and decisions are discussed and derived in Arabic.
IS AVOIDING CONFLICT OF INTEREST MORE IMPORTANT THAN KNOWLEDGE SHARING?
One wish that I had for the Shariah Governance is the composition of Shariah Committee itself. While the limitation of service of not more than 9 years is good for an IFI (to encourage rotation in the industry), I still feel the knowledge growth and development of Shariah Committees may not be as fast as the anticipated industry growth. What more, I feel that the limitation of a Shariah scholar to only serve in 1 (one) Islamic Bank, 1 (one) Takaful Company, and 1 (one) Islamic Development Bank do not allow the sharing of knowledge between entities and industries. Perhaps there is a concern where there could be a conflict of interest? I do not know. All I know is that globally, it is common to see one advisor sitting on multiple boards; and from the knowledge gathering for being in multiple boards, can be a substantial resource for the IFI.
WHY NOT THE CURRENT STRUCTURE?
In my opinion, there is a real shortage of knowledge between the old guards and the new challengers in the areas of Islamic Banking. What I see nowadays are issues being re-discussed again and again, and some have been discussed at length in different forums or decades earlier, with solid resolutions. The new scholars do not have the full understanding of history, background and context on many issues (some of which have already been discussed), and the older guard of very prominent scholars are not able to share the history, perspective, experience, background and earlier discussions on matters of Islamic Banking. This gap remains huge as the young scholars run to catch up in terms of the understanding that the older guards have. This resulted in many real, new and current issues being somewhat ignored as past issues are again discussed.
SO WHAT IS MY DREAM TEAM FOR A SHARIAH COMMITTEE?
In my perfect world, I would love to see a combination of the following:
- The Shariah Committee Chairman. Senior person in the industry leading the committee, with vast experience of Islamic Banking operations, as well as Shariah Qualified and conversant in written and spoken Arabic. Must have leadership qualities to be able to manage the Shariah Committee.
- Prominent Scholar. One prominent scholar should sit in as part of the Shariah Committee for the purpose of providing guidance, mentoring, advising and coaching to new Shariah Committee members and Industry Experts. This scholar should come from a list of 10-15 “A-Rated” Shariah scholars who have been in the industry for more than 15 years. Must have some capacity in BNM’s Shariah Advisory Council or is a Consultant with a reputable Shariah research house. Must have international exposure or sitting in an international Shariah board. Is allowed to sit in up to 5 (five) local Islamic Banks, Development Banks or Takaful Companies. Also conversant in Arabic, both written and spoken.This list of “A-Rated” Shariah scholars must be maintained or endorsed by BNM, just like how the Shariah Advisory Council (SAC) of BNM is maintained.
- Combination of Shariah Scholars and Industry Experts. Can be appointed based on expertise and academic background with strong background in research. Must be Shariah Qualified and conversant in written and spoken Arabic. For Industry Experts, must be a specialist in the give area and have sufficient experience. This group is to be groomed to be included into the “A-Rated” Shariah Scholars upon completion of tenure. Training and exposure to be given, with the assistance of the Prominent Scholar, on how to upscale and up-skill the knowledge in Islamic Banking. And to be included into the “A-Rated” Shariah Scholars list, the scholars must undergo an overseas / international attachment with an international Islamic Bank as part of the Shariah Committee, perhaps for a period between 3 months to 6 months. This attachment should ideally be sponsored by BNM as part of the development of the Shariah Scholars exposure and capabilities.
Conclusion : The Shariah Governance Policy Document remains a strong upgrade from the previous SGF and should provide a more serious undertone to the overall workings of a Shariah Committee. This shall lead to stronger governance but I am not convinced on the development of Shariah Committees with the limitations imposed on appointments into Islamic Financial Institutions.
Wallahualam.








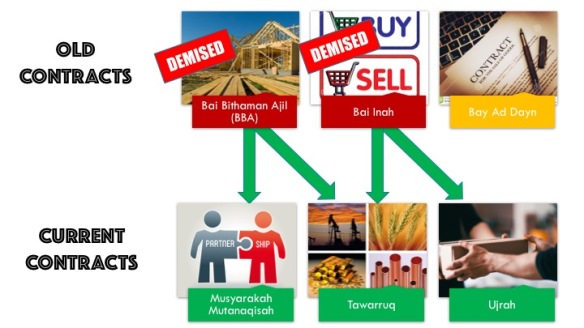





 When we first started the Islamic Banking journey in late 1990’s and early 2000s, BNM encouraged a lot of product innovation from Banks as there were no existing guidelines. We looked at the various structures that provides the desired outcomes and discussed with Shariah Committee on the design and component of products without breaching Sharia rules. BNM was supportive on us developing these “innovative” products. Some may have been controversial (such as Bai Inah, Bay Ad Dayn, Wadiah and Bai Bithaman Ajil) but it encourages discussions alongside the mantra that “whatever is not explicitly prohibited, is permissible“. Sometimes we were forced to think outside of the box, especially for sophisticated products mirroring conventional. We also received support from Sharia Committees whom temporarily approved “innovative” products with the understanding that over time, a better solution were developed as replacements.
When we first started the Islamic Banking journey in late 1990’s and early 2000s, BNM encouraged a lot of product innovation from Banks as there were no existing guidelines. We looked at the various structures that provides the desired outcomes and discussed with Shariah Committee on the design and component of products without breaching Sharia rules. BNM was supportive on us developing these “innovative” products. Some may have been controversial (such as Bai Inah, Bay Ad Dayn, Wadiah and Bai Bithaman Ajil) but it encourages discussions alongside the mantra that “whatever is not explicitly prohibited, is permissible“. Sometimes we were forced to think outside of the box, especially for sophisticated products mirroring conventional. We also received support from Sharia Committees whom temporarily approved “innovative” products with the understanding that over time, a better solution were developed as replacements. Making Tawarruq as the “all-problems-solved” structure is having an unfortunate result to the industry. While the issuance of the Policy Documents as a reference was to galvanise the development of various Islamic contracts, the Banks have an easy way out in Tawarruq. Now, the rest of the contracts are in danger of being sidelined in favour of continuous development in Tawarruq.
Making Tawarruq as the “all-problems-solved” structure is having an unfortunate result to the industry. While the issuance of the Policy Documents as a reference was to galvanise the development of various Islamic contracts, the Banks have an easy way out in Tawarruq. Now, the rest of the contracts are in danger of being sidelined in favour of continuous development in Tawarruq. Malaysia is in danger where I foresee that one day the industry itself will became the absolute global expert in Tawarruq and Commodity Murabaha. With Bursa Suq Al Sila as the leading commodity trading platform for the country, backed by the government (as a national bourse), the Tawarruq structure is expected to evolve into an efficient Islamic-structure engine. The processes of Commodity Murabaha will become seamless, and may even integrate into a Bank’s core banking system, the operation for buying and selling commodity will become commonplace and familiar, and this will result in effective processing, awareness of Shariah risks, compliance to trading requirements and well as reduction in overall operational risks.
Malaysia is in danger where I foresee that one day the industry itself will became the absolute global expert in Tawarruq and Commodity Murabaha. With Bursa Suq Al Sila as the leading commodity trading platform for the country, backed by the government (as a national bourse), the Tawarruq structure is expected to evolve into an efficient Islamic-structure engine. The processes of Commodity Murabaha will become seamless, and may even integrate into a Bank’s core banking system, the operation for buying and selling commodity will become commonplace and familiar, and this will result in effective processing, awareness of Shariah risks, compliance to trading requirements and well as reduction in overall operational risks.





















